A Configure La Fonera A. Configure La Fonera IP Address: This field shows La Foneras IP address. Note that its the same address you typed to access the Management Console. Configure your public network You can change the public network settings from this section of the Management Console. 192.168.1.128 is a Private IP Address for use only inside of a Private Network. This address can be used by routers, modems, and other many devices. You are trying to.
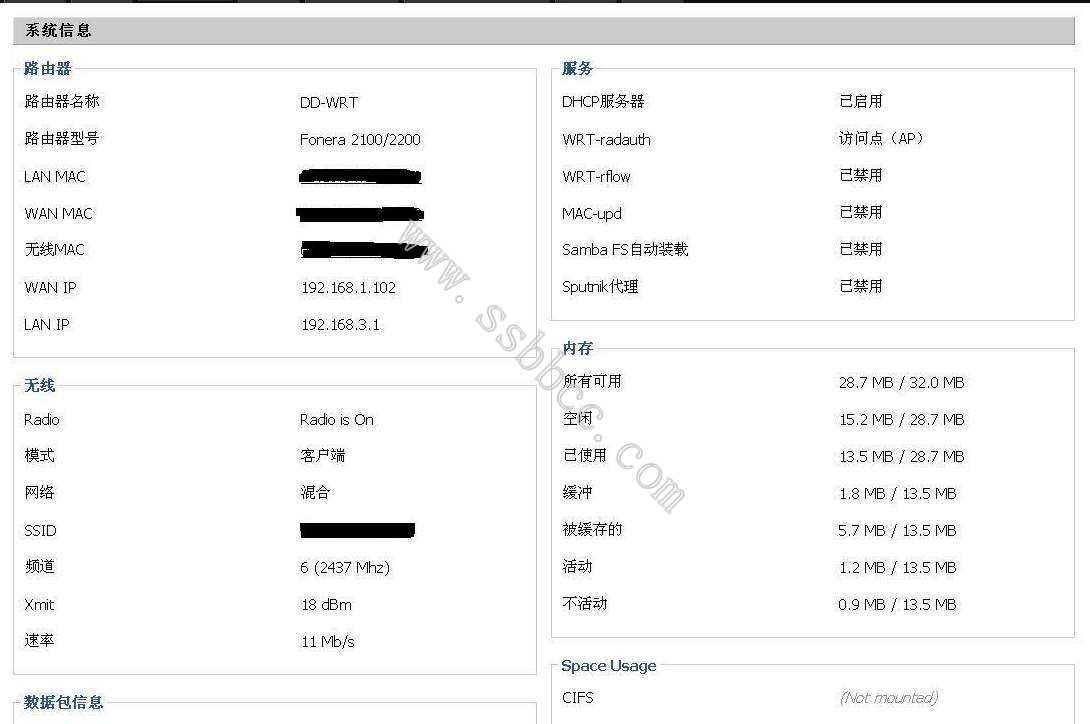
[SOLVED]How to change wireless mac addresses of Fonera???
| DD-WRT Forum Forum Index ->Atheros WiSOC based Hardware |
View previous topic :: View next topic | |||||
| Author | Message | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| drpepperONE DD-WRT Novice Joined: 02 Dec 2007 Posts: 17 Location: http://www.wifi-ita.com/forum/ |
| ||||
| Sponsor <=' td='> | |||||
| drpepperONE DD-WRT Novice Joined: 02 Dec 2007 Posts: 17 Location: http://www.wifi-ita.com/forum/ |
| ||||
| mazilo DD-WRT User Joined: 10 Jun 2006 Posts: 385 |
| ||||
| drpepperONE DD-WRT Novice Joined: 02 Dec 2007 Posts: 17 Location: http://www.wifi-ita.com/forum/ |
| ||||
| mazilo DD-WRT User Joined: 10 Jun 2006 Posts: 385 |
| ||||
| drpepperONE DD-WRT Novice Joined: 02 Dec 2007 Posts: 17 Location: http://www.wifi-ita.com/forum/ |
| ||||
| drpepperONE DD-WRT Novice Joined: 02 Dec 2007 Posts: 17 Location: http://www.wifi-ita.com/forum/ |
| ||||
| Simon DD-WRT Guru Joined: 20 Jul 2007 Posts: 612 |
| ||||
| goldserve DD-WRT User Joined: 07 Jun 2006 Posts: 115 |
| ||||
| drpepperONE DD-WRT Novice Joined: 02 Dec 2007 Posts: 17 Location: http://www.wifi-ita.com/forum/ |
| ||||
| maybeme DD-WRT Novice Joined: 21 Apr 2007 Posts: 15 |
| ||||
| drpepperONE DD-WRT Novice Joined: 02 Dec 2007 Posts: 17 Location: http://www.wifi-ita.com/forum/ |
| ||||
| drpepperONE DD-WRT Novice Joined: 02 Dec 2007 Posts: 17 Location: http://www.wifi-ita.com/forum/ |
| ||||
| drpepperONE DD-WRT Novice Joined: 02 Dec 2007 Posts: 17 Location: http://www.wifi-ita.com/forum/ |
|
| DD-WRT Forum Forum Index ->Atheros WiSOC based Hardware | All times are GMT |
Navigation
| You cannot post new topics in this forum You cannot reply to topics in this forum You cannot edit your posts in this forum You cannot delete your posts in this forum You cannot vote in polls in this forum You cannot attach files in this forum You cannot download files in this forum |
- 1FLASHING
- 1.2Mac OS X
- 2CONFIGURATION
FLASHING
NEW: Gargoyle Flash Fon Utility
Gargoyle project includes a Flash Fon utility that works similarly as EasyFlash, but works on MacOSX, Linux and Windows
Mac OS X
Since EasyFlash isn't available for Max OS X, we do this manually (FON2200 + ethernet only): Smart interactive whiteboard.
1. Set IP address of your Mac:
antifuchs says: this does not work reliably on Leopard. What does work is: In Network.prefpane, Make a new network location, make inactive every device except ethernet; set ethernet config to 'Manual', configure IP address 192.168.1.254. Then select that location as your current location.
2. Enable tftp
Alternative 1:Get TFTPServer, point it to the directory that contains the firmware; it needs to be world-read/writable; you can let that program fix permissions for you.
Altenative 2: Use the tftp server which comes with Mac OS X:
3. Copy OpenWRT files to tftp dir:
These files are typically what you want to use:
- openwrt-atheros-2.6-vmlinux.lzma
- openwrt-atheros-2.6-root.squashfs
4. Upload the firmware
Two methods here: The lazy approach, and flashing it manually. I recommend doing it by hand at least once to be able to debug the lazy approach if it goes wrong.
Flashing manually
Get access to RedBoot
See also http://forum.openwrt.org/viewtopic.php?pid=63402.
fonera an den strom, wenn das 2te led zu blinken beginnt:
danach ctrl+c

-> You should now have a 'RedBoot>' prompt. If not, rinse and repeat.
Flash new kernel and filesystem images in RedBoot:
In RedBoot (assuming you configured the machine with the tftp server to 192.168.1.254):
Reboot
You are now where EasyFlash ends.Wait for the boot to finish and telnet to 192.168.1.1 and set a root password.
Flashing automatically (the lazy approach)
Get this expect script (written by Antifuchs and Marius):https://whatever.metalab.at/user/kintel/fonera/flashit.expect
Usage:
1. Start script: ./flashit.expect
Optionally, you can give kernel and squashfs files as parameters if they don't have the default filenames
2. Connect and power up the Fonera
3. When you see stuff happening, go for lunch.
When the script exits (and you see no error message), you can safely reboot the box and telnet to 192.168.1.1
Windows/Linux (easyflash):
- Flashing Utility
- Linux/Unix: ap51-flash-fonera-1.0-42
- Windows: ap51-flash-fonera-gui-1.0-42.exe
Passendes Tool runterladen.
- System Images
die beiden runterladen.
Jetzt kommts.
- Linux/Unix Vista
- Fonera mit Ethernet-Patchkabel an eth0 anstecken.
- Linux/Unix unter Windows
ap51-flash-fonera-gui-1.0-38.exeals Administrator ausführen - Strom an den Fonera anstecken
Der Fonera schickt nun beim hochfahren einen ARP request raus, das Flashtool wartet darauf und tut dann seine Magie.Der ganze Flashvorgang dauert rund _15_ Minuten.Zuerst sieht man die IP vom Router Dann steht da was von
Fertig.
Danach hat der Fonero die IP 192.168.1.1 und ist über TELNET erreichbar.Happy hacking.
Flashen direkt aus laufendem OpenWRT
Wenn OpenWRT bereits läuft kann man auch direkt auf eine neue Version updaten bzw. diese über die grade laufende Version drüber flashen.
ABER VORSICHT! Das geht nur wenn die neuen Kernel- und Dateisystemimages gleich groß oder kleiner sind als die die aktuell installiert sind, sonst ist nicht genug Platz frei! In dem Fall müssen die Partitionen ohnehin neu angelegt werden - also eine der anderen hier beschriebenen Updateroutinen verwenden!!
Zuerst per SSH einloggen, dann:
Danach einfach neu starten (Stecker ziehen), per Telnet einloggen und den SSH Zugang neu aktivieren (siehe unten)
set password after flashing
note: after flashing, the fingerprint of the router changes. in that case delete the old entry for 192.168.1.1 from your ssh known_hosts file:
On Windows you can use PuTTY for the SSH connection.
CONFIGURATION
default network configuration files
| file | description |
|---|---|
| /etc/ethers | specifying static IP addresses via DHCP |
| /etc/dnsmasq.conf | configures DNS masquerading |
| /etc/hosts | maps IP-address to hostname |
| /etc/networks | maps network addresses to network name |
| /etc/protocols | maps protocol to port number; see IANA for a complete list |
| /etc/config/dhcp | configures dhcp server |
| /etc/config/dropbear | configures ssh |
| /etc/config/firewall | configures firewall |
| /etc/config/network | configures network interfaces |
| /etc/config/system | |
| /etc/config/wireless | configures wireless lan adapter |
/etc/ethers
This file maps a given MAC-address to an IPv4-Address via DHCP. Example:
Hint: You get the MAC-address using ipconfig -all on Windows or by using ifconfig on Linux/Unix.
/etc/hosts
maps IP address to full domain names, local domain names, and local hostnames. Example:
Hint: you can also use a hosts file to block bad sites; see also custom hosts files
/etc/networks
configures the names and addresses of networks. this file is used by the route command. Example:
/etc/protocols
Usually you don't touch that.
/etc/config/network
See OpenWRT Kamikaze Manual for setting up basic network configuration
- Example 0:
Routing between Ethernet and WLAN
Note: Routing is enabled by default, so you usually don't have to configure routing tables.
- Example 1:
Bridging Ethernet and WLAN
- Example 2:
Bridging multiple Ethernet ports
/etc/config/wireless
See OpenWRT Kamikaze Manual for setting up basic wireless network configuration
- Example 0:
Routing Ethernet and WLAN without encryption
Note: Routing is enabled by default, so you usually don't have to configure routing tables.
- Example 1:
Bridging Ethernet and WLAN with WPA2-PSK-encryption
- Example 2:
Configure WDS
- WDS Access Point (WDS-AP; first node)
- WDS-Station (WDS-STA; all other nodes)
- Notes on WPA2-Encryption
For WPA2-Encryption you must install hostapd on Access Points
as well as wpa-supplicant on WDS-Stations
FIXME: Encryption also may only work on interface ath0. Please share your experience here.
INSTALLING PACKAGES
After you have successfully configured a connection with the internet, you can load additional software packages using ipkg.
FIXME: If you compiled OpenWRT yourself, you can register your computer as the package repository
- install packages
- uninstall packages
- Fette ipkg repositories
- http://downloads.openwrt.org/kamikaze/packages/mips/
- http://ipkg.k1k2.de/packages/
MESH NETWORKS
For Mesh Networks you have to install one of
- olsrd (may produce routing loops, but standardized and most widely deployed)
- batman (also included in the robin firmware; does not scale for big networks; beta)
- babel (also works with wired connections; beta)
on all your nodes.
FIXME: write a howto
CLONING
How to clone (or backup) a Fonera:
1. Get this expect script (written by Marius):https://whatever.metalab.at/user/kintel/fonera/clone.expect
2. Set up your fonera so you can ssh in without a password:
- Copy your computer's ~/.ssh/id_dsa.pub (or equivalent) to the Fonera
- On the Fonera:
Fonera Ip Address Finder
3. Run the script on your computer
4. The backup is now made to the files clone.lzma and clone.squashfs. These can be used to reflash another fonera to become an identical copy.
Assumptions: The fonera lives at 192.168.1.1, the root prompt contains a '#', a normal openwrt is flashed on it.
NB! This has not been tested very well, so use with caution until it's been more quality assured.Bugreports are welcome :)
kyrah says: I've tried cloning my Fonera (running OpenWrt) using these instructions, resulting in #fail:Looks like the rootfs_data partition is overwritten when firstboot is run. Must investigate further.
SOFTWARE
- software zum flashen + packages .
- http://download.berlin.freifunk.net/fonera/
- Buildchain
- http://wiki.openwrt.org/BuildingPackagesHowTo
svn co https://svn.openwrt.org/openwrt/tags/kamikaze_7.09- http://forum.openwrt.org/viewtopic.php?pid=31794#p31794
- Fette ipkg repositories
- http://downloads.openwrt.org/kamikaze/packages/mips/
- http://ipkg.k1k2.de/packages/
HARDWARE
- LCD am fonera?
- http://www.lefinnois.net/wpen/index.php/2007/11/11/lcd-screen-for-la-fonera/
- I2C bus?
- http://www.lefinnois.net/wpen/index.php/2007/05/13/i2c-bus-for-la-fonera/

-> You should now have a 'RedBoot>' prompt. If not, rinse and repeat.
Flash new kernel and filesystem images in RedBoot:
In RedBoot (assuming you configured the machine with the tftp server to 192.168.1.254):
Reboot
You are now where EasyFlash ends.Wait for the boot to finish and telnet to 192.168.1.1 and set a root password.
Flashing automatically (the lazy approach)
Get this expect script (written by Antifuchs and Marius):https://whatever.metalab.at/user/kintel/fonera/flashit.expect
Usage:
1. Start script: ./flashit.expect
Optionally, you can give kernel and squashfs files as parameters if they don't have the default filenames
2. Connect and power up the Fonera
3. When you see stuff happening, go for lunch.
When the script exits (and you see no error message), you can safely reboot the box and telnet to 192.168.1.1
Windows/Linux (easyflash):
- Flashing Utility
- Linux/Unix: ap51-flash-fonera-1.0-42
- Windows: ap51-flash-fonera-gui-1.0-42.exe
Passendes Tool runterladen.
- System Images
die beiden runterladen.
Jetzt kommts.
- Linux/Unix Vista
- Fonera mit Ethernet-Patchkabel an eth0 anstecken.
- Linux/Unix unter Windows
ap51-flash-fonera-gui-1.0-38.exeals Administrator ausführen - Strom an den Fonera anstecken
Der Fonera schickt nun beim hochfahren einen ARP request raus, das Flashtool wartet darauf und tut dann seine Magie.Der ganze Flashvorgang dauert rund _15_ Minuten.Zuerst sieht man die IP vom Router Dann steht da was von
Fertig.
Danach hat der Fonero die IP 192.168.1.1 und ist über TELNET erreichbar.Happy hacking.
Flashen direkt aus laufendem OpenWRT
Wenn OpenWRT bereits läuft kann man auch direkt auf eine neue Version updaten bzw. diese über die grade laufende Version drüber flashen.
ABER VORSICHT! Das geht nur wenn die neuen Kernel- und Dateisystemimages gleich groß oder kleiner sind als die die aktuell installiert sind, sonst ist nicht genug Platz frei! In dem Fall müssen die Partitionen ohnehin neu angelegt werden - also eine der anderen hier beschriebenen Updateroutinen verwenden!!
Zuerst per SSH einloggen, dann:
Danach einfach neu starten (Stecker ziehen), per Telnet einloggen und den SSH Zugang neu aktivieren (siehe unten)
set password after flashing
note: after flashing, the fingerprint of the router changes. in that case delete the old entry for 192.168.1.1 from your ssh known_hosts file:
On Windows you can use PuTTY for the SSH connection.
CONFIGURATION
default network configuration files
| file | description |
|---|---|
| /etc/ethers | specifying static IP addresses via DHCP |
| /etc/dnsmasq.conf | configures DNS masquerading |
| /etc/hosts | maps IP-address to hostname |
| /etc/networks | maps network addresses to network name |
| /etc/protocols | maps protocol to port number; see IANA for a complete list |
| /etc/config/dhcp | configures dhcp server |
| /etc/config/dropbear | configures ssh |
| /etc/config/firewall | configures firewall |
| /etc/config/network | configures network interfaces |
| /etc/config/system | |
| /etc/config/wireless | configures wireless lan adapter |
/etc/ethers
This file maps a given MAC-address to an IPv4-Address via DHCP. Example:
Hint: You get the MAC-address using ipconfig -all on Windows or by using ifconfig on Linux/Unix.
/etc/hosts
maps IP address to full domain names, local domain names, and local hostnames. Example:
Hint: you can also use a hosts file to block bad sites; see also custom hosts files
/etc/networks
configures the names and addresses of networks. this file is used by the route command. Example:
/etc/protocols
Usually you don't touch that.
/etc/config/network
See OpenWRT Kamikaze Manual for setting up basic network configuration
- Example 0:
Routing between Ethernet and WLAN
Note: Routing is enabled by default, so you usually don't have to configure routing tables.
- Example 1:
Bridging Ethernet and WLAN
- Example 2:
Bridging multiple Ethernet ports
/etc/config/wireless
See OpenWRT Kamikaze Manual for setting up basic wireless network configuration
- Example 0:
Routing Ethernet and WLAN without encryption
Note: Routing is enabled by default, so you usually don't have to configure routing tables.
- Example 1:
Bridging Ethernet and WLAN with WPA2-PSK-encryption
- Example 2:
Configure WDS
- WDS Access Point (WDS-AP; first node)
- WDS-Station (WDS-STA; all other nodes)
- Notes on WPA2-Encryption
For WPA2-Encryption you must install hostapd on Access Points
as well as wpa-supplicant on WDS-Stations
FIXME: Encryption also may only work on interface ath0. Please share your experience here.
INSTALLING PACKAGES
After you have successfully configured a connection with the internet, you can load additional software packages using ipkg.
FIXME: If you compiled OpenWRT yourself, you can register your computer as the package repository
- install packages
- uninstall packages
- Fette ipkg repositories
- http://downloads.openwrt.org/kamikaze/packages/mips/
- http://ipkg.k1k2.de/packages/
MESH NETWORKS
For Mesh Networks you have to install one of
- olsrd (may produce routing loops, but standardized and most widely deployed)
- batman (also included in the robin firmware; does not scale for big networks; beta)
- babel (also works with wired connections; beta)
on all your nodes.
FIXME: write a howto
CLONING
How to clone (or backup) a Fonera:
1. Get this expect script (written by Marius):https://whatever.metalab.at/user/kintel/fonera/clone.expect
2. Set up your fonera so you can ssh in without a password:
- Copy your computer's ~/.ssh/id_dsa.pub (or equivalent) to the Fonera
- On the Fonera:
Fonera Ip Address Finder
3. Run the script on your computer
4. The backup is now made to the files clone.lzma and clone.squashfs. These can be used to reflash another fonera to become an identical copy.
Assumptions: The fonera lives at 192.168.1.1, the root prompt contains a '#', a normal openwrt is flashed on it.
NB! This has not been tested very well, so use with caution until it's been more quality assured.Bugreports are welcome :)
kyrah says: I've tried cloning my Fonera (running OpenWrt) using these instructions, resulting in #fail:Looks like the rootfs_data partition is overwritten when firstboot is run. Must investigate further.
SOFTWARE
- software zum flashen + packages .
- http://download.berlin.freifunk.net/fonera/
- Buildchain
- http://wiki.openwrt.org/BuildingPackagesHowTo
svn co https://svn.openwrt.org/openwrt/tags/kamikaze_7.09- http://forum.openwrt.org/viewtopic.php?pid=31794#p31794
- Fette ipkg repositories
- http://downloads.openwrt.org/kamikaze/packages/mips/
- http://ipkg.k1k2.de/packages/
HARDWARE
- LCD am fonera?
- http://www.lefinnois.net/wpen/index.php/2007/11/11/lcd-screen-for-la-fonera/
- I2C bus?
- http://www.lefinnois.net/wpen/index.php/2007/05/13/i2c-bus-for-la-fonera/
- SD card am fonera?
- http://www.larsen-b.com/Article/262.html
- http://phrozen.org/fonera.html
Fonera Ip Address Labels
- GPIO kernel modul
- http://mobileaccess.de/fonera/gpio/
- http://daubau.net/proc_gpio/
Fonera Ip Address Ip
- Fertig compiliertes GPIO kernelmodul im feschen .ipk + src
- Media:Kamikaze_7.09_GPIOkmod.tar.gz
